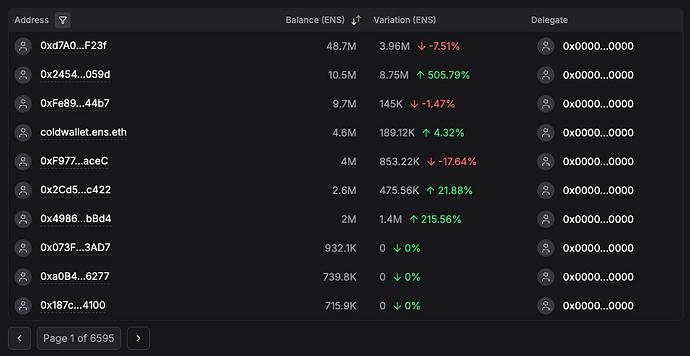
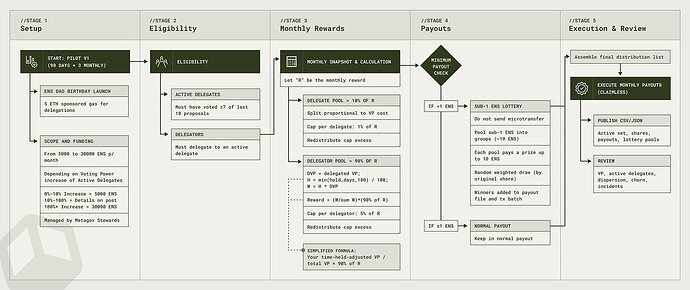
We’ll use this thread to post all our past and future quarters updates under the scope of ENS service provider.
Q1/Q2 report
Summary
Our journey began with our proposal to the ENS DAO, where we outlined our vision for enhancing ENS. The challenge we decided to first work on was related to off-chain and L2 resolvers. After Vitalik’s tweet, it became clear that it was important.
Our approach is to create solutions and standards that enhance the whole ecosystem and do not fragment it by competing with other platforms. We want to support both existing and new builders.
Overview
Implementing a standard, not creating a competing platform. Let’s understand what that means:
Namestone is a service that creates and manages off-chain subdomains through an API. Data is stored in a database. Before performing any write operation, you should read their docs and know how to communicate with the API.
This is true for every other subdomain issuer you see: cb.id, base.eth, linea.eth, namespace, etc.
By having projects that use and contribute to this standard, we can build applications that can interact with all of these providers without needing to understand the implementation details for each one.
Success in this initiative means having significant players adopting the standard and having the ENS dapp and ensjs implementing the ENSIP.
Transparency: build in public
This is one of blockful’s core values. Not only are the repos open-source, but so are the task management, planning, and track records. You can see all the tasks done in the first semester, with all card descriptions, related pull requests, team discussions, and estimates keeping all the development and research contracted by the DAO accountable.
Foundation and Research
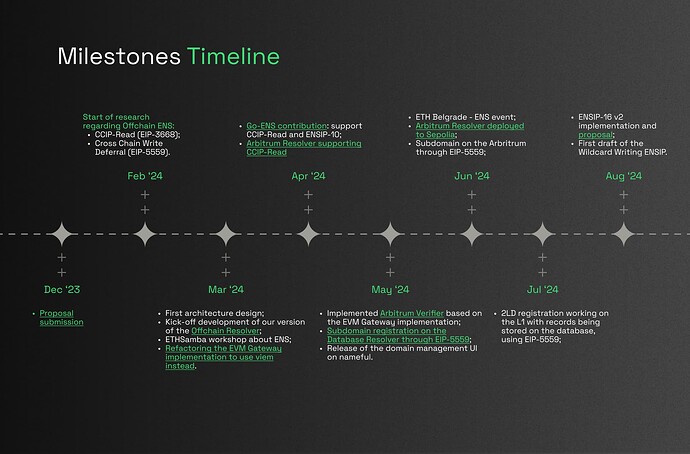
Following the proposal, we dove deep into research on Offchain ENS considering it would bring the most value to the ecosystem. Our team studied the intricacies of CCIP-Read (EIP-3668) implementation and investigated the potential of Cross Chain Write Deferral (EIP-5559). This foundational research shaped our understanding and approach to off-chain solutions.
We then moved into the development phase, creating the initial version of our Offchain Resolver. This was a significant step forward, translating our research and design into a functional implementation. During this process, we encountered a challenge with the Optimism integration due to updates in EVM Gateway data verification (addition of Fault Proofs on OP). We then pivoted our focus to Arbitrum, ensuring continued progress in our off-chain resolver development.
Good standards and research can only be done if you get hands-on, so we explored each off-chain resolver step to understand improvement opportunities.
Technical Contributions
External resolver (repo)
The goal of the external resolver repo is to be the industry standard for off-chain domains (using DBs and L2s), implementing the new ENSIP and past ENSIP support, with interoperability as the core value. This led us to the development of our own version of the CCIP-Gateway based on the Chainlink implementation as well as contract interfaces that made easier the implementation for multiple contexts.
We then launched our first version of the Arbitrum Resolver with CCIP-Read support, followed by the implementation of the Arbitrum Verifier based on the EVM Gateway. This further solidified our off-chain resolver’s capabilities within the Arbitrum ecosystem.
Go ENS (pull request)
Our team contributed to the Go-ENS library, adding support for CCIP-Read and ENSIP-10 to improve the broader ENS ecosystem. Also, a public bounty of 0.5 ETH helped prioritize it.
User-Facing Developments (repo)
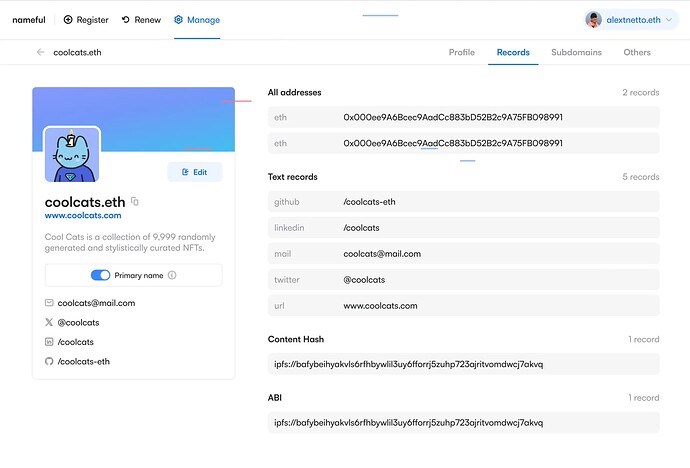
Recognizing the importance of user accessibility, we began the development of the nameful dapp. This initiative aimed to bring our off-chain solutions closer to end-users, making them more accessible and user-friendly, as well as serving as proof-of-concepts for both the off-chain reading and writing standards we’re developing.
Our work on the Database Resolver saw several key achievements. We completed the EIP-5559 implementation, achieved the first subdomain registration using this protocol, and successfully deployed the resolver to the Sepolia testnet. These milestones marked significant progress in our off-chain capabilities.
To enhance user interaction with our solutions, we launched the domain management UI on nameful. This interface made it easier for users to manage their ENS domains using our off-chain features.
Expanding Capabilities
Our Arbitrum integration reached new heights as we deployed the Arbitrum Resolver to Sepolia testnet and registered the first subdomain on Arbitrum through EIP-5559. These achievements demonstrated the practical application of our off-chain solutions in a Layer 2 environment.
We then enhanced our Gateway functionality by implementing support for writing multicall. This improvement increased the efficiency of our off-chain operations, allowing for more complex interactions.
In a significant step towards bridging on-chain and off-chain capabilities, we registered the first 2LD on L1 with records stored in the database. This milestone showcased the seamless integration between traditional ENS infrastructure and our off-chain solutions.
Standards and Specifications
As already mentioned, the major purpose of the external resolver implementation is establish a standardized flow for managing offchain writing in the ENS ecosystem, creating an universal interface that can be applied across various scenarios of offchain domain storage.
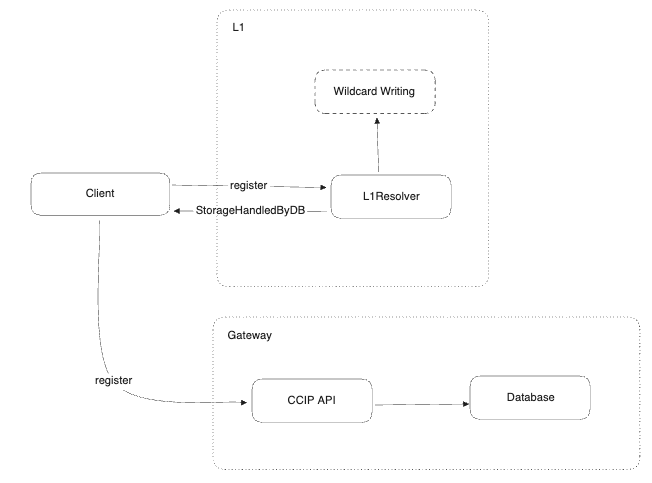
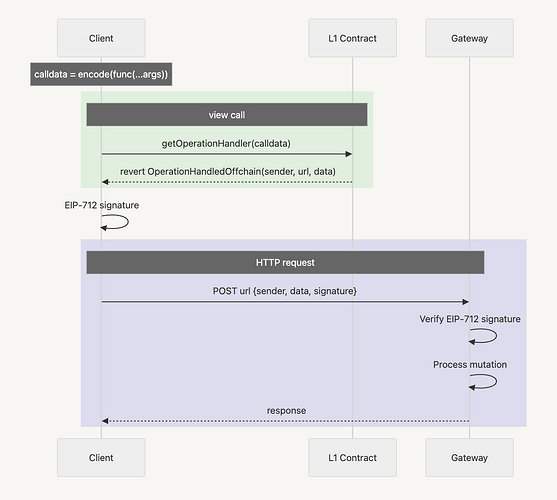
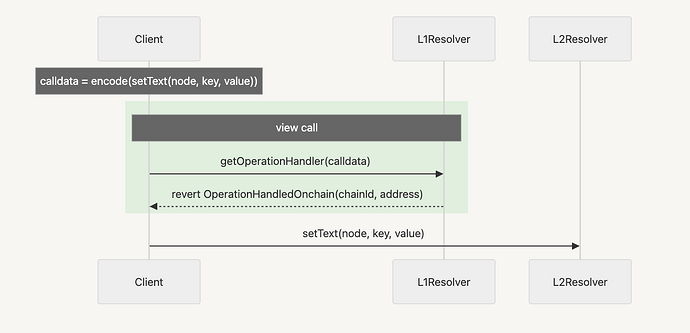
The key value the standard brings is the communication with the L1 redirecting the request to the given destination by relying on the EIP-5559. The complete flow can be visualized on the following diagrams:
L2 subdomain registering [WIP]
Database subdomain registering
During the development of the nameful dapp, we faced a challenge in integrating offchain domains with existing ENS components. This led us to propose improvements to the existing ENSIP-16 (Offchain Metadata API). Our proposal aims to enhance the developer experience by reducing the number of requests required to fetch all the data of a given domain. The proposal is currently under discussion in the ENS community, and we’re actively gathering feedback.
Finally, we drafted the first version of what we’ve called Wildcard Writing ENSIP, a standard interface that standardizes the off-chain writing methods. This contribution, which has yet to be posted on the ENS forum, aims to achieve the interoperability we mentioned at the beginning of the report.
Community education
As an initiative to educate and involve the Latin American community in the ENS and ETH ecosystem, we conducted a workshop at the ETH Samba hackathon in Rio de Janeiro. The workshop showcased major ENS features and provided a step-by-step guide on how to set up a domain.
More to come on that in the following months.
Governance security
As mentioned in our proposal, we are reviewing the call data for each executable proposal. EP 5.12 was the only one that wasn’t possible due to its size and details. We will create a more official report platform through a forum thread to make sure this work is accountable.
Other contributions not related to service provider scope
Being closer to ENS as an organization allowed our research team to also analyze the governance in depth (which is our primary expertise as blockful), which led to research that resulted in the creation of the Security Council. We’re finishing a blog post that will outline more of this work for securing the DAO.
Looking Ahead
As we continue our journey, we remain committed to:
- Refining and formalizing our off-chain standards based on community feedback.
- Working on the adoption of these standards with major players, ENS app and ENSjs.
- Expanding partnerships and integrations to increase ENS adoption.
- Understand what brings the most value for ENS and the community, adapting our protocol research and scope of work for optimal value generation.
We’re grateful for the support of the ENS DAO and community throughout this journey. We look forward to further collaboration as we work together to enhance and expand the ENS ecosystem.
![L2 subdomain registering [WIP]](https://discuss.ens.domains/uploads/db9688/optimized/2X/c/cdc3bd31677396be7ae4b3d1d26b4e98b2f3cb4b_2_690x332.png)